Product Categories
- Related Products (0)
- Main products (5)
- Minoxidil (1)
- Finasteride (1)
- Dutasteride (1)
- RU58841 (1)
- Way316606 (1)
- New Research (4)
- CB-03-01 (1)
- KX-826 (1)
- SM04554 (1)
- Pyrrolidinyl Diaminopyrimidine (1)
Both Dutasteride and Finasteride reduce DHT production by inhibiting the action of 5α-reductase, thereby preventing hair loss. Finasteride was the first FDA-approved product to treat hair loss based on the 5α-reductase pattern, and Dutasteride came about 10 years later than Finasteride, so while we were learning about Dutasteride, You can’t avoid comparing it to Finasteride. So what are the effects and side effects of their treatment of scalp hair loss, and which one is better?
5α-reductase is a key factor in the conversion of testosterone to DHT, which includes type I and type II 5α-reductase. Type I 5α-reductase is found primarily in most skin areas, but also in the scalp and liver. Type II 5α-reductase is present in hair follicles, prostates, and epididymis. Finasteride is a selective inhibitor of 5α-reductase, which mainly inhibits the action of type II 5α-reductase. Dutasteride is a dual 5α-reductase inhibitor that inhibits both type I and type II 5α-reductase.
Finasteride selectively inhibits the action of type II 5α-reductase and reduces the conversion of testosterone to DHT by type II 5α-reductase.
Dutasteride is a dual inhibitor of type I and type II 5α-reductase that reduces the conversion of testosterone to DHT by type I and type II 5α-reductase.
Therefore, from the perspective of mode of action, Finasteride only inhibits the action of type II 5α-reductase, while Dutasteride inhibits both type I and type II 5α-reductase. Therefore, Dutasteride has a wider range of action than Finasteride and should be more effective in treating hair loss.
Finasteride reduces circulating DHT levels by about 70% and Dutasteride reduces circulating DHT levels by about 99%.
Finasteride reduced scalp DHT levels by about 38% and Dutasteride reduced circulating DHT levels by about 54%.
Based on their reduced circulating DHT levels and scalp DHT levels, Dutasteride is more effective than Finasteride in treating DHT hair loss.
Testosterone is a male sex hormone, mainly through the positive feedback of HPTA (hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis) stimulated release, in the male body to maintain a state of dynamic balance. In addition to its own effects, 5% to 10% of testosterone is converted to DHT (dihydrotestosterone) by 5α-reductase, and about 0.2% of testosterone is converted to estrogen by interaction with aromatase.
DHT is a more potent androgen than testosterone and has a higher affinity for androgen receptors, about 5 times greater than testosterone.
Male pattern alopecia, also known as male androgenic alopecia, illustrates the relationship between hair loss and androgens, and DHT is the more potent androgen.
Androgenic alopecia affects 30-50% of men over the age of 50. This hair loss occurs in a repeatable pattern, resulting in hair loss at the temples, top of the head, and mid-forehead skin. It is hereditary, meaning that genetic factors account for about 80% of susceptibility. When men have a family history of hair loss, they are more likely to start losing their hair at a younger age than their peers. Therefore, if you have a family history of hair loss, early awareness of the effects of hair loss and early intervention will be much better than treating hair loss after it starts to appear.
The main role of DHT is in the male embryo and adolescence, during which DHT negates the differentiation and maturation of male characteristics. After adolescence, DHT is not without a role, as an androgen, it is useful in maintaining libido and sexual function, as well as in skeletal muscle. We hope that DHT will act on these sites, for example in skeletal muscle. As an androgen, when DHT acts in skeletal muscle, it promotes bone health and an increase in muscle mass.
However, the part where DHT works is related to the distribution of 5α-reductase in various parts of the body. 5α-reductase is mainly distributed in the prostate, epididymis, skin, hair follicles, etc., and therefore, DHT levels are higher in these areas.
We want DHT to work more efficiently than testosterone in skeletal muscle, but in these locations, there is no 5α-reductase to convert testosterone into DHT.
Testosterone is produced in the testicles and then circulates throughout the body, so the concentration of testosterone is greatest around the testicles. The prostate is an organ close to the testes and has high levels of testosterone. Therefore, a large amount of testosterone is converted into DHT by the 5α-reductase in the prostate gland, which is one of the reasons for the high incidence of prostate hyperplasia in men as they age.
There are also high levels of 5α-reductase in the skin and hair follicles, and when circulating testosterone reaches these locations, it is converted into the more potent androgen DHT, which binds to the androgen receptors in the hair follicle and affects the size and cycle of the hair follicle, thereby affecting hair growth and quality, causing hair loss.
Thus, after puberty, when males are fully sexually developed, some of the effects of DHT accumulation begin to show. So it’s not like you start losing your hair after middle age. For people with hereditary hair loss, hair loss begins at the age of 20, and it is only after middle age, when you can see the scalp, that you realize that the hair loss has been serious.
Early detection, early treatment, in order to better preserve the existing hair. Both Finasteride and Dutasteride treat hair loss by reducing the production of DHT, and apparently Dutasteride reduces DHT more effectively than Finasteride. This conclusion is based on the mode of action of Finasteride vs Dutasteride. Is there any relevant trial that proves that Dutasteride is better?
In a randomized placebo-controlled trial, the effects of Dutasteride versus Finasteride were compared. In the study, 917 male patients with AGA were given oral doses of 0.02mg Dutasteride, 0.1mg Dutasteride, 0.5mg Dutasteride, 1mg Finasteride and placebo daily. At week 24, the 0.5mg Dutasteride group significantly increased hair count and improved hair growth. Dutasteride was more effective at increasing hair volume than Finasteride and placebo, and the results were dose-dependent.
In 2 observational studies, oral administration of 0.5mg of Dutasteride per day resulted ina greater increase in total hair after 24 weeks, with a difference of 7.1 hairs per square centimeter compared to 1mg of Finasteride per day, indicating that oral Dutasteride was more effective.
In another study that included 576 participants, the researchers compared average changes in total hair count, photo evaluations, and participants’ post-treatment evaluations and found statistically significant differences in treatment outcomes. Dutasteride is more effective than Finasteride in the treatment of AGA.
The actual effectiveness of each hair loss medication varies from person to person, with some patients responding to Dutasteride and not to Finasteride. So, if AGA men have no effect with Finasteride, they can try Dutasteride to treat hair loss.
The dose of Dutasteride is 0.5mg per day, orally.
When Dutasteride was used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia in men, the effect of 0.5mg per day was comparable to Finasteride’s effect of 5mg per day.
When Dutasteride was used to treat hair loss in men, a dose of 0.5mg per day was more effective than Finasteride’s 1mg per day.
In the Dutasteride trial, when the dose was gradually increased from 0.02mg to 0.5mg, the 0.5mg daily dose produced a better effect than the lower dose, and the effect was dose-dependent.
Therefore, the dose of Dutasteride is 0.5mg per day. As with Finasteride, the daily dose of Dutasteride should be taken at the same time each day, regardless of whether it is with a meal, but do not use a double dose.
Dutasteride is used as frequently as Finasteride, once a day, but their half-lives vary widely. Finasteride has a half-life of 5-6 hours, with a half-life of more than 8 hours in older men.
Dutasteride has a long half-life of 4-5 weeks, with a longer half-life in older men. Because Dutasteride has a long half-life, it takes a longer time to reach a stable concentration in the body, so the effect time is slightly slower than that of Finasteride. At the same time, after stopping the drug, it will remain in the body for a long time, about 4-6 months. People treated with Dutasteride cannot donate blood for at least six months.
Dutasteride has a longer half-life of 4-5 weeks, and it takes about 3-4 months to achieve stable blood levels, so the improvement is not seen until 3-6 months after treatment with Dutasteride. The full effect of the drug requires consistent use for 1 year. If you don’t see any improvement after using Dutasteride for a year, you may be a non-responder and continuing to use it won’t produce results.
Because DHT is continuously produced in the body, Dutasteride needs to be used for a long time to continuously prevent hair loss and maintain existing gains.
If you need to stop using Dutasteride, you should stop the drug slowly and continue it until your hair begins to thin again, or use another hair growth product.
Side effects of oral Dutasteride are similar to those of Finasteride, mainly decreased libido, sexual dysfunction, gyno.
In a one-year comparative trial of Dutasteride 0.5mg/day versus Finasteride 5mg/day, there was no significant difference in the incidence of the most common drug-related adverse events between the two groups. More than 2% of the adverse events were impotence and decreased libido, and the other adverse events were less than 2%.
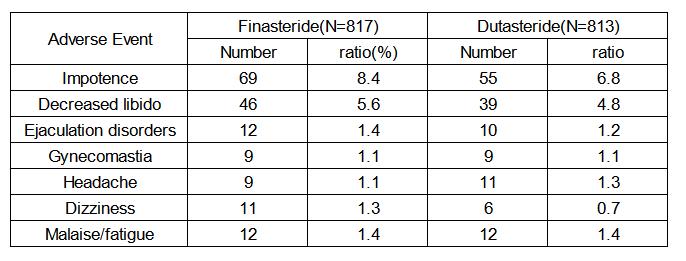
In the clinical trial of 6,729 male patients, 9% experienced erectile dysfunction (compared to 5.7% in the placebo group), 3.3% experienced decreased libido (1.6% in the placebo group), and 1.9% experienced breast enlargement (1% in the placebo group). The quality of a man’s sperm is also affected. Most of these side effects disappear after 3 to 4 months of discontinuation.
Dutasteride may also cause an allergic reaction, resulting in a rash and swelling of the face, tongue or throat.
The side effects caused by 5α-reductase inhibitors are known as “post-Finasteride syndrome”.
The use of Finasteride masks the early symptoms of prostate cancer, while Dutasteride does not.
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, participants were 8,000 men from 42 countries aged 50 to 75 years with PSA levels of 2.5-10 ng /mL and normal pre-study prostate biopsy results.
After 4 years, Dutasteride reduced the risk of prostate cancer by 23 percent compared to a placebo.
The reduction of prostate cancer by Dutasteride was associated with its inhibition of both type I and type II 5α-reductase. Type I 5α-reductase is low in benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), but is dominant in prostate cancer and overexpressed in some prostate cancers. Type II 5α-reductase is dominant in normal and benign hyperplasia of prostate tissue. Therefore, when Dutasteride inhibits the action of type I 5α-reductase, the type I 5α-reductase cannot express the corresponding action in prostate cancer, thus reducing the probability of prostate cancer.
In a study of AGA men, 90 patients were divided into three groups, the first group was injected with 0.005% Dutasteride, the second group was injected with 0.005% Dutasteride+ D-panitol + biotin + pyridoxine, and the third group was injected with saline. After 5 months, patients in the first and second groups had significantly increased hair diameter compared to the third group, and the second group showed significant new hair growth. In the first and second groups, no changes in sperm parameters were observed.
In a treatment for female hair loss, 126 female patients received 0.005% Dutasteride+ D-panthenol + biotin + pyridoxine injection, and compared with saline treatment, after 4 months, 63% of patients receiving Dutasteride+ additive showed significant improvement in hair.
The trial showed that low-dose injections of Dutasteride had a hair growth effect with fewer side effects and did not affect the quality of men’s sperm.
A 2014 study comparing Finasteride and Dutasteride in 917 men aged 20 to 50 at different stages of hair loss showed that men who took Duasteride had thicker hair than those who took Finasteride. The average number of hairs in the target area was higher.
The researchers compared the effects of oral Minoxidil, Finasteride and Dutasteride and concluded that Dutasteride was more likely to be the most effective in treating male pattern baldness.