Product Categories
- Related Products (0)
- Main products (5)
- Minoxidil (1)
- Finasteride (1)
- Dutasteride (1)
- RU58841 (1)
- Way316606 (1)
- New Research (4)
- CB-03-01 (1)
- KX-826 (1)
- SM04554 (1)
- Pyrrolidinyl Diaminopyrimidine (1)
There are two drugs approved by the FDA to treat androgenic alopecia AGA, Minoxidil and Finasteride 1mg.Finasteride works in a different way than Minoxidil, in that finasteride prevents hair loss by reducing circulating levels of DHT, as detailed below.
Finasteride is a 5α-reductase inhibitor, which, as the name suggests, works by inhibiting the action of 5α-reductase.
The reason for the development of 5α-reductase inhibitors is an individual case of a genetic mutation that prevents the synthesis of DHT(dihydrotestosterone) due to a lack of 5α-reductase, resulting in prostate agenesis and male pattern alopecia. This led biologists to realize the role of DHT in prostatic hyperplasia and baldness.
In the above example, DHT is a factor that must be associated with hair loss, or the most important cause of hair loss. So how does DHT cause hair loss?
Hair loss caused by DHT is associated with hair follicles. Hair follicles are cyclical, and a growth cycle goes through three phases: the anagen phase, the catagen phase, and the Telogen phase. The accumulation of androgens (especially DHT) in the hair follicle can affect the growth cycle of the hair follicle, making the growth period shorter and extending the resting period, resulting in the loss of the previous batch of hair before the new batch of hair has grown. The buildup of DHT in the hair follicle also produces inflammation, leading to the hair follicle miniaturization and eventually degeneration. Therefore, the continuous accumulation of DHT leads to an increasingly large area of hair loss.
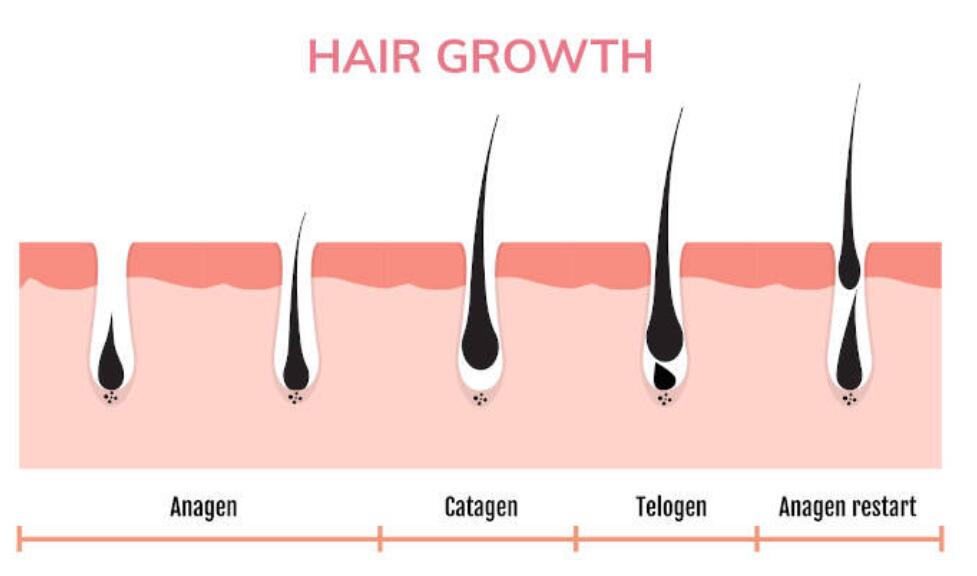
The main source of DHT in the body is testosterone, and the enzyme that converts testosterone into DHT is 5α-reductase. 5α-reductase is mainly found in the skin, hair follicles, and prostate. Finasteride inhibits the action of 5α-reductase, reducing the rate at which testosterone is converted to DHT, thereby reducing circulating DHT levels, including DHT in hair follicles. Finasteride Treat hair loss caused by DHT by reducing DHT.
Finasteride works by inhibiting 5α-reductase, but because there are two types of 5α-reductase (type I and type II) in the body, and finasteride only inhibits the action of type II 5α-reductase, it does not reduce DHT levels 100%.
Type I 5α-reductase is mainly found in the sebaceglands of most skin areas, including the scalp and liver, converting about one-third of the circulating DHT. Type II 5α-reductase is mainly found in the hair follicles, prostate, epididymis, seminal vesicles, etc., and is responsible for converting about two-thirds of the circulating DHT.
Studies have shown that Finasteride reduces circulating DHT levels by 68% to 72% by inhibiting the action of type II 5α-reductase. By reducing DHT levels by about 70%, hair loss can be reduced in some AGA patients, but the effect may not be significant in some people.
In two studies of balding men by Merck, men treated with finasteride 1mg showed significant increases in hair volume at 6 and 12 months, while men treated with placebo showed significant hair loss at baseline. After one year, ina 1-inch circle, finasteride 1mg had a negative interest rate plus 107 hairs more than the placebo group, compared to placebo. After 2 years, finasteride 1mg increased the number of hairs in the same area by 138 more than placebo. Among balding men treated with finasteride 1mg, the greatest improvement in hair volume was achieved in the first 2 years. After five years of continuous treatment, hair counts remained above baseline, while men in the placebo group continued to lose their hair. At the end of the 5-year treatment period, the difference in the number of hairs between the 1mg group taking finasteride and the placebo group was 277.
In the trial data published by Merck, the increase in hair growth in men treated with finasteride 1mg ranged from 48% to 66%.
Results from a Phase III clinical study of 1,879 men suggest that for a large proportion of men with male pattern hair loss, oral finasteride 1mg daily can promote hair growth and prevent further hair loss. There is evidence that improvements in hair number reported after one year are maintained during two years of treatment. Among men with hair loss on the top of the head, the overall picture showed that 48 percent of finasteride recipients had improved hair growth at 1 year and 66 percent at 2 years, compared with 7 percent of placebo recipients at each time point.
In addition, the men’s hair counts showed that after two years, 83 percent of the finasteride group and 28 percent of the placebo recipients had no further hair loss compared to baseline.
A study of finasteride 1mg in patients with vertex baldness assessed the effects of scalp hair volume and growth in patients with vertex baldness, involving 212 participants, over a 48-week period. After 48 weeks, men with vertex baldness who received 1mg of finasteride had 7 and 18 more hairs and hair growth, respectively, in an area of 1 square centimeter, while men with vertex baldness who received placebo had 10 and 9 fewer hairs, respectively. The difference in total hair number within a 1 cm2 area was 17 hairs and the difference in hair number was 27 hairs.
This trial demonstrated the therapeutic effect of finasteride 1mg in men with vertex baldness, in addition to maintaining existing hair without loss, promoting the growth of new hair and increasing the total amount of hair.
finasteride 1mg for hair loss has been tested in long-term and high-dose trials.
In the long-term trial of finasteride 1mg, the duration was up to 5 years. Treatment-related adverse events were reported in 7.7% of patients treated with 1 mg of finasteride per day, compared with 7.0% of patients treated with placebo. The overall incidence of sexual dysfunction (including decreased libido, ejaculation disorders, and erectile dysfunction) was significantly higher in the finasteride group than in the placebo group (3.8% vs 2.1%). All sexual adverse events were reversed after discontinuation of treatment, and many adverse events resolved in patients who continued treatment.
In the high-dose trial of finasteride 1mg, single doses up to 400 mg per day and multiple doses up to 80 mg per day over three months were well tolerated and did not lead to any significant adverse effects in clinical studies.
Finasteride 1mg has been approved by the FDA, and side effects are manageable when used in doses as directed.
We are talking about Finasteride 1mg, so, for hair loss, the dose of Finasteride is 1mg a day, orally.
The FDA has approved two levels of Finasteride. One is Finasteride 5mg, named Proscar, for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men. The other is Finasteride 1mg, named Propecia, used to treat male pattern hair loss (AGA).
So when your doctor prescribes Finasteride to treat hair loss, the dosage of Finasteride is 1mg per day by mouth.
In the Finasteride trial, oral administration of 0.2mg per day reduced circulating DHT levels by 68.6 percent, while oral administration of 5mg per day reduced circulating DHT levels by 72.2 percent. From this data, the difference between 68.6% and 72.7% is not large, and the difference between the two doses of 0.2mg and 5mg is still relatively large. Therefore, if you want to use Finasteride more safely, 0.2mg of oral Finasteride per day is feasible.
In summary, Finasteride doses range from 0.2mg to 1mg per day.
Finasteride is taken orally, usually at the same time each day, if you miss the day’s dose, you can take a refill within 6 hours, if more than 6 hours, do not take a refill, and do not take a double dose the next time.
In a clinical trial of Finasteride that lasted up to five years, overall improvements in hair from Finasteride 1mg were seen as early as three months and continued for five years compared to the placebo group.
When using Finasteride 1mg to treat male pattern hair loss, improvement is usually seen after 3 months of continuous use, and significant changes can be seen after 1 year. If you’ve used Finasteride 1mg for more than 1 year and haven’t seen any improvement, it’s proven to be ineffective for you and continuing to take it probably won’t help.
If you have experienced significant improvements in hair volume after use, continuing to take Finasteride can help to consistently help you reduce hair loss.
Will I be able to maintain my hair when I stop using Finasteride after I have improved my hair?
Finasteride prevents hair loss by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to DHT by the enzyme 5α-reductase. Testosterone is the male sex hormone that maintains men’s physiological function and physical health, and as long as testosterone and 5α-reductase are always present in the body, DHT will continue to be produced. If you stop using Finasteride, the circulating testosterone produced every day will still affect the growth of hair follicles. Therefore, Finasteride is a drug that needs to be used continuously over a long period of time.
If you stop using finasteride after achieving improvement, within a year, you may lose the hair that regrew while taking finasteride.
70% to 80% of women with hyperandrogen will show hypertrichosis. This is because androgens increase the rate of hair growth and transform short, fine, light baby hair (vellus hair) into thick, long and dark hair (terminal hair).
When androgens decrease, the growth of new hair decreases, as does the growth of existing hair.
Finasteride reduces DHT throughout the body, not only in the scalp, but also in the skin. When androgens in a woman’s skin decrease, hair growth decreases. Therefore, Finasteride is also being developed to treat hirsutism in women.
When women take Finasteride to treat hirsutism, the dose is usually 2.5-5mg per day.
Finasteride is a proven drug that is relatively safe to use within prescribed doses. This is not to say that it is without side effects, Finasteride has some common side effects. Some people will ignore these side effects because they prefer to get hair growth, while others may choose other hair loss medications because of these side effects.
Finasteride works by reducing the production of DHT, which is useful in the human body.
DHT is responsible for the sex differentiation of the male genitalia during embryogenesis and the development and maturation of secondary sexual characteristics during puberty. If a pregnant woman uses Finasteride, it may affect the development of the embryo. If a child uses Finasteride, it may affect the development and maturation of secondary sexual characteristics. Men using Finasteride should keep the medication out of reach of children and pregnant women.
When men use Finasteride, the conversion of testosterone to DHT decreases and, relatively speaking, the body’s testosterone levels increase. More testosterone translates into more estrogen. When estrogen levels rise and DHT levels fall, changes in sex hormone levels can affect a man’s libido and erectile function. In the Finasteride trial, the probability of men experiencing reduced libido was about 4 percent, and the probability of sexual dysfunction was about 2 percent.
Gynecomastia (gyno) is caused by excessive production of estrogen. Because finasteride reduces the conversion of testosterone into DHT, more of it is converted into estrogen, but estrogen does not increase indefinitely due to the body’s dynamic balance of testosterone levels. The probability of gyno in men is also very low, about 1.5%.
High estrogen levels are common among male bodybuilders, and male bodybuilders are also very adept at dealing with this symptom.
Finasteride is metabolized by the liver, so you should be aware of possible liver damage during use. Finasteride should be chosen carefully for patients with poor liver itself.Finasteride is not metabolized in the kidneys and therefore has no effect on the kidneys.
Postural hypotension was also observed in patients with hair loss treated with Finasteride 1mg.
Although Finasteride blocks the action of androgen DHT, it is not an antiandrogen in itself, has no affinity for androgen receptors, and does not affect estrogen receptors. Finasteride had no effect on LH&FSH, HPTA, cortisol, thyroid, plasma lipid profile, etc.
Finasteride 1mg is a 5α-reductase inhibitor that prevents and treats hair loss by reducing the production of DHT. As the first oral hair growth drug approved by the FDA, Finasteride has a proven safety profile. Finasteride is primarily used to treat male pattern baldness and is effective in patients with baldness.